Sunday, October 30, 2022
Free Trade is Fraud. There is Nothing Free About the Carbon Cost Dumped on the Atmosphere. 2022-1-30. Jorma Antero Jyrkkanen
Is Trade Free? Not in any aspect. Every movement of goods anywhere in the world has an environmental cost due to the energy consumed. That energy is used in making the infrastructure of trade, the transportation equipment, spent in the delivery and distribution.
932 MILLION TONNES(1000 KGS)=932 BILLION KGS CO2 IS PROOF FREE TRADE IS DEADLY GREENWASHING FRAUD. TO THESE EMISSIONS ONE HAS TO ADD THE GREENHOUSE GAS COST OF SMELTING THE STEEL AND ALUMINUM FOR SHIPS AND CONTAINERS AND THE ENERGY USED IN WELDING THEM TOGETHER. CLIMATE BUSTING UNFREETRADE.
Wednesday, October 26, 2022
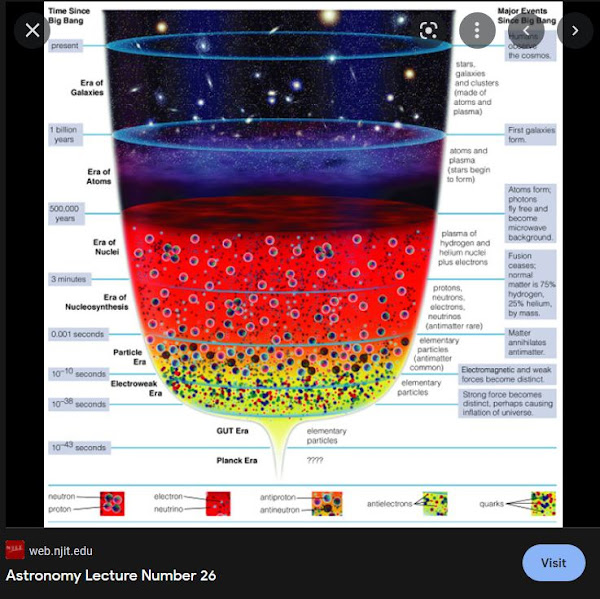
Evolution is the Creator. GENERAL THEORY OF UNIVERSAL EVOLUTION. 5 April 2012 Jorma Antero Jyrkkanen, BSC, PDP
My observation that our quarks, gluons and electrons are ancient universe
assembled by Physical and Organic evolution into a primate that is now pondering itself, the Parent Universe and Evolution as the
Creator is the material foundation for the dawning of a new age of philosophical-scientific-spiritual enlightenment that allows us to be proud and noble in our discovered connection to the our mother universe. We fabricated in far off times imaginary mythical Creator Gods (https://www.godchecker.com/) many in our own image during our pre-scientific genesis. This is I think my most important conclusion. We are the universe. We are the mind of the universe pondering and speaking about itself and have even created a new quasi universe, cyberspace. We are ephemeral and transient and will go extinct one day and return to our quarks, gluons and electrons.
General Theory of Universal Evolution by Jorma Jyrkkanen
GENERAL THEORY OF UNIVERSAL EVOLUTION
5 April 2012
My Theory was Presented at the April 12 2012 meeting of The Central Okanagan Naturalists Club to a full house as The Evolution Bit Darwin Couldn't Possibly Know, from Higgs to Comparative Genomics. More has emerged recently on the role of chance and epigenetics. http://www.okanagannature.org/
Thank you ladies and gentlemen for this opportunity to share my limited understanding of this vast subject with you. There are insights here for philosophy, human relations and our relationship with all life and even our place in the universe. A different paradigm emerges from these considerations than the one we have inherited through cultural evolution born in ignorance and mythology. I am humbled by the enormity of it all.
PHYSICAL EVOLUTION, THE CREATION OF THE FRAMEWORK FOR ORGANIC EVOLUTION
Big Bang-release of eternal energy, expansion, cooling, 4 Forces peeled off. The laws of the universe emerge with pure energy from the singularity.
-Higgs energy field, is everywhere, imparts mass to particles. I like to think of bottom spin on a cue ball stuttering on a rutted table top made of energy density which raises energy of the ball, entangling it with space time which translates into mass. Excitation of the Higgs field is the Higgs Boson. M Theory says strings moving through 11 dimensions causes mass. Einstein E=mc^2
-Since the energy density is the fabric of space time I imagine quantum mechanics is entangled with space time through the Higgs interaction creating the phenomenon Einstein called relativity and which I conjecture imaginatively as gravitational entanglement, the conjugation of quantum mechanics and relativity.
-Standard model, quantum mechanics, quantum entanglement and gravity, relativity. It is all about the behavior of energy and how it gathers and interacts.
-The DNA of the physical universe is the shape-set of the curled invisible dimensions of string theory. Each shape-set determines the properties of a possible universe. There are 10^500 possible shapes. (I owe this idea to my online Physics Professor, Dr. Leonard Susskind Felix Bloch Professor of Physics, Princeton)
-Quark gluon gamma ray soup. The Big Bang diversion via expansion, cooling, layers of the four forces diverge.
-Protons and anti-protons form
-Symmetry splitting, more protons than antiprotons->proton (matter) universe. They p differ in half lives enabling matter to dominate. Quarks gather in protons and neutrons. Creation of atomic nuclei.
-Gases cool, gravity collects into early galaxies and suns. Convergence.
-Galaxies, suns, supernovas are born leading to fusion, fission, beta decay nucleosynthesis of elements, periodic table is filled. Our building ingredients mfg'd (O, C, N, S, Fe, Ca, Mg, Na, K, ...) ie created. Creation of new atomic species from gathering protons and neutrons into atoms by electron shells (SPDF orbitals).
-Supernovas blow elements into surrounding universe in another Big Bang divergence, expansion carries them off into foamy matrix, gravity collects ejecta into solar systems, planets in another convergence inside galaxies. Supernovas happen every day. Periodic table elements being re-created universe wide constantly.
NUCLEOSYNTHESIS OF ATOMS
-Quantum mechanics creates molecules for life both in space and on earth and in space, ex. AA, nucleic acids, ribose. Varieties exist just like with Darwin's finches.
-Asteroids, comets deliver molecules of life to planets and some are created by Urey Miller synthesis. In Goldilocks planets there is biomolecular synthesis of AA, proteins, nucleic acids; ongoing also in other regions of the universe in various stages. Combinants converge. Super varieties formed.
-Physical evolution creates materials and opportunity for infinite chance events to diversify and a framework for them to happen and exist within. Given infinite time and space and randomness, the least improbable event becomes certitude.
-Physical evolution is the creator of the universe and science is the way to know it. We are inseparably part of it all and the energy in our quarks and electrons is as ancient as the big bang, 13.7 bya.
-The universe is homogenous enough to assert definitively that these physical evolutionary synthetic processes are broadly similar and universe wide such as to set the stage for organic evolution throughout the cosmos with vagaries of serendipity helping dictate the exact results whence cometh my assertion of the General Theory. Supernovae function vis a vis nucleosynthesis and cooling related force delamination phase changes are likely not affected by modest changes in homogeneity nor isotropy even in an accelerating universe.
We are quarks, gluons, electrons and pure energy at root. We are a microcosm of the universe assembled from itself by physica evolution and organic evolution. Physical evolution is the creator of the universe and sets the stage for the evolution of life if chance permits and it does.
ORGANIC EVOLUTION; THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MOLECULES OF LIFE AND LIFE ITSELF
-Urey-Miller biomolecular synthesis, CH4, NH3, H2, H2O, (HCN)
-life starts, Pr-Lipid, RNA-Pr lipid, DNA-RNA-Protein,
-Watson Crick DNA RNA elucidation as the genetic code of life on earth
ONE THEORY OF ORIGINS
Abstract
How and where did life on Earth originate? To date, various environments have been proposed as plausible sites for the origin of life. However, discussions have focused on a limited stage of chemical evolution, or emergence of a specific chemical function of proto-biological systems. It remains unclear what geochemical situations could drive all the stages of chemical evolution, ranging from condensation of simple inorganic compounds to the emergence of self-sustaining systems that were evolvable into modern biological ones. In this review, we summarize reported experimental and theoretical findings for prebiotic chemistry relevant to this topic, including availability of biologically essential elements (N and P) on the Hadean Earth, abiotic synthesis of life's building blocks (amino acids, peptides, ribose, nucleobases, fatty acids, nucleotides, and oligonucleotides), their polymerizations to bio-macromolecules (peptides and oligonucleotides), and emergence of biological functions of replication and compartmentalization. It is indicated from the overviews that completion of the chemical evolution requires at least eight reaction conditions of (1) reductive gas phase, (2) alkaline pH, (3) freezing temperature, (4) fresh water, (5) dry/dry-wet cycle, (6) coupling with high energy reactions, (7) heating-cooling cycle in water, and (8) extraterrestrial input of life's building blocks and reactive nutrients. The necessity of these mutually exclusive conditions clearly indicates that life's origin did not occur at a single setting; rather, it required highly diverse and dynamic environments that were connected with each other to allow intra-transportation of reaction products and reactants through fluid circulation. Future experimental research that mimics the conditions of the proposed model are expected to provide further constraints on the processes and mechanisms for the origin of life.
This line of work posits the criticality of cyanide, alpha keto acids, ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Research Paper. Origins of building blocks of life: A review; Author NorioKitadai, ShigenoriMaruyama
Prior thinking was insprired by the Urey Miller Experiments utilizing methane, hydrogen, water vapour and carbon dioxide and aldehydes. Nucleotides can be created from fairly simple ingredients.
-Molecular genetics determines all life has RNA or DNA and RNA and Proteins
-Venter and Colleagues elucidate human genome and many many more proving the DNA/RNA based genetic code programs all like on earth and common ancestral origins for all life.
-Codification in DNA proves relatedness, degree of similarity in DNA sequence, function relates to degree of relatedness
-bacteria earliest life forms (side effect that bacteria feel right at home in us/on us).
-bacteria evolved photosynthetic pigments
-early bacteria evolved glycolysis ie energy fm sugars
-mitochondria bacters (Rickettsias, SAR II) evolved metabolism of pyruvate via citric acid cycle. 36 ATP vs 2 ATP without mitochondria. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA cause myopathies. What we got from our primal bacteria cell merging with mitchondria was energy for work. Primal cell may have also been a ciliate as suggested by oour lung cilia and sperm tails which are near identical to Eukaryote cilia in electron microgrpah cross section. Mitochondrial Endosymbiosis probably with an Archaea cell producing the 3 branches of higher life.
-metazoa evolved by endosymbiosis of p amoeboid cells and mitochondria (SAR II, Ricketsia bacterai) and these evolved into higher animals forms, Protista, Invertebrata, via mergers and acquisitions and lateral transfers, ongoing.
-plants evolved by a primal cell merging with endosymbiont mitochondria bacteria and chloroplast bacteria
-higher early animals evolved p by Garstang hypothesis process inverts to verts; protogeny of Ascidians, where larva became an adult
-Chordates to Vertebrates cephalization with mouth and sensory organs in the front end, gills, jaws, bilateral symmetry, post anal tail, segmented myomeres, cartilagenous notochord, dorsal hollow neural tube, coelom, egenes
-Fish (Crossopterigia) evolvedctoderm, mesoderm, endoderm, tissue development by HOX fins into feet and lungs (Dipnoi, lung fish) for gulping air colonizing land as Amphibia
-Some Amphibia evolved the amniotic egg that was able to withstand drying conditions forming reptilia and Synapsids which later formed Therapsids and later Mammals and us. A very ancient one found to date was The Hylonomus lyelli, 312 million years old and was discovered in a petrified tree stump near Joggins in the Bay of Fundy, 250 kilometres north of Halifax. The fossil was uncovered by Nova Scotian geologist John William Dawson in 1859 but was handed over to the British Museum around the turn of the century.Apr 24, 2011.
Evolution of Amniotes
The first amniotes evolved from their amphibian ancestors approximately 340 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. The Amniote Egg.
This is a stem amniote, Protoclepsydrops. Chances are good we once looked like this for a considerable length of time. Looks a tad like Pederpes from the Romer's Gap.
The early amniotes diverged into two main lines soon after the first amniotes arose. The initial split was into synapsids and sauropsids. Synapsids include all mammals, including extinct mammalian species. Synapsids also include therapsids, which were mammal-like reptiles from which mammals evolved. The middle one below is our synapsid ancestor skull form.
-Reptilia ruled til the big asteroid 66.046 million years ago which gave opportunities to mammals. They (Ex Morganuccodon) gave rise to ears, large brains, complex behaviour in mammals w hair, placenta, live immature young, warm blooded, milk and birds. A stem Eutherian (true mammals-our group) Juramia.
Juramaia Skeleton and note dentition had evolved diversity.
- Tree shrew types survived the asteroid to become loris, lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys. Gliding Tree Lemurs as exemplified by the the Colugo are the extant living ancestors of the Primates, our line.
-Those evolved into primates which evolved into us bags of up/down quarks held together w gluons wrapped in whizzy electrons. We invented the Gods to explain how and why but then discovered science, the new how and why. We ponder Higgs, the Genetic code of all life and evolutionary creation.
-Darwin showed surplus production, variants, competition, nature selects, fittest survive. We have since learned about the role of luck. It matters.Primate Evolution produced considerable diversity.
-Venter made a synthetic organism come to life. He picked DNA he wanted, put them together and stuck em in an empty yeast capsule and it worked, did what he wanted.
-Geneticists showed populations of genes carried traits and these are acquired from ancestors via linear transfer and also form lateral transfer ex HERV's, bacterial DNA
-All living things are kin if you go back far enough. The triplet code for amino acids is constant in all life and this is the strongest evidence all life had a common ancestor and we are all kin, yes evry living thing is kin to us.
-We are a composite of a lot of lateral gene insertions, duplications, mutations, deletions, mergers and and linear injections, a chimaera if you will. All living things are composites. Each merger gave us a set of traits that we have for genetic baggage with fit ones being fixed, bad ones stored, altered or deleted. We are a committee of genomes and genes.
-Science is about the creation and the creation process and we could properly call it creation science.
-Life begins at the subatomic level when assemblages of quarks begin to cannibalize other assemblages to extract energy and replacement parts. It ceases when the cannibalization stops.
SUMMARY OF PHYSICAL AND ORGANIC EVOLUTION INTO THE GENERAL THEORY OF UNIVERSAL EVOLUTION
The energy in our atoms is of infinite age and p has always existed by energy conservation laws and needed no creator. Our mother and father were the big bang, supernovas and suns acted upon by gravity, molecular synthesis induced by quantum mechanical effects acting with the four forces, and earth, dashed by asteroids and comets carrying life's molecules, and the organic soup on earth, fired by lightening and fires.
A homogenous isotropic universe would have the conditions for life being constantly created by supernovas dispersed approximately as we see spiral galaxies dispersed. this may not be true at boundary conditions. There is an acceleration towards a preferred region of space suggesting periferal anisotropy.
The same atoms that are associated with life, and physical processes like nucleosynthesis and quantum mechanics are everywhere in the universe suggesting myriads of opportunities for life elsewhere. Given infinite time and random rolls of the dice the most improbable event becomes certitude.
We are a bag of quarks surrounded by electrons causing tiny dimples in space time which in turn gives us our mass through gravity. We spend most of eternity in the atomic and molecular states which only move according to Newton's Laws and a tiny fraction in a virtual mobile form. We can be completely boiled down into three bags, on with up quarks, another with down quarks, a bottle of gluon and a bag of electrons.
We are both infinitely old energy, 13+ byo quarks and electrons, atoms of star stuff, created by physical and organic evolution into the mind of the universe, now pondering the universe and our creator, universal evolution.
We humans made the thousands of Gods to explain all this before science. All living things are family. The universe is our home and womb, Earth is our heaven.
Energy is eternal. All the laws of physics were contained in the singularity. Was it intelligent and benevolent? it was pregnant with possiblity and thats one thing we can count on. Evolution is pretty cruel from time to time and flawed so its hardly benevolent.
So what are humans and why are we here? I call this the cypher. The how is the why and science explains how and this tells us why things are what they are. To know why, find out how. It answers an enoromous philosophical void. https://humanorigins.si.edu/education/introduction-human-evolution
WHAT THEN ARE WE HUMANS? 1 March 2012
The energy in our atoms is of infinite age and p has always existed by energy conservation laws and needed no creator. Our mother and father were the big bang, supernovas and suns acted upon by gravity, molecular synthesis induced by quantum mechanical effects acting with the four forces, and earth, dashed by asteroids and comets carrying life's molecules, and the organic soup on earth, fired by lightening and fires.
A homogenous isotropic universe would have the conditions for life being constantly created by supernovas dispersed approximately as we see spiral galaxies dispersed. this may not be true at boundary conditions. There is an acceleration towards a preferred region of space suggesting periferal anisotropy.
The same atoms that are associated with life, and physical processes like nucleosynthesis and quantum mechanics are everywhere in the universe suggesting myriads of opportunities for life elsewhere. Given infinite time and random rolls of the dice the most improbable event becomes certitude.
We are a bag of quarks surrounded by electrons causing tiny dimples in space time which in turn gives us our mass through gravity. We spend most of eternity in the atomic and molecular states which only move according to Newton's Laws and a tiny fraction in a virtual mobile form.
We are both infinitely old energy, 13+ byo quarks and electrons, atoms of star stuff, created by physical and organic evolution into the mind of the universe, now pondering the universe and our creator, universal evolution.
All living things are family. The universe is our home and womb, Earth is our heaven.
Energy is eternal. All the laws of physics were contained in the singularity. Its likely chance alone enabled life in our universe? it was pregnant with possiblity and thats one thing we can count on. Evolution is pretty cruel from time to time and flawed so its hardly benevolent or intelligent. It just works like a hot dam.
Physical and organic evolution, universal evolution, are the creator, governed by the laws of nature. We are e the universe become conscious pondering itself. We are the mind of the universe in very real sense. We made stories in mythology and the gods to explain the how and why and now science teaches us how the laws of nature made everything from energy.
I dedicate this Theory to my Late Brother Dougy Jyrkkanen wo died in a tragic accident as a Youth. We discussed investigation of this topic when paddling down the Skagit River in a raft while doing phenology and deer studies for Slaney while I was a Zoology student at UBC.
Copyright 2012 Jorma Jyrkkanen. All rights reserved.
Tags: Evolution, physical evolution, organic evolution, General Theory of Universal Evolution, Jorma Jyrkkanen
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
Antibiotics Discussion. Risks and Benefits. Mitochondrial Poisons? Discussion by Suárez-Rivero JM, Pastor-Maldonado CJ, et al. 2022-10-25. Jorma Jyrkkanen
The discovery and application of antibiotics in the common clinical practice has undeniably been one of the major medical advances in our times. Their use meant a drastic drop in infectious diseases-related mortality and contributed to prolonging human life expectancy worldwide. Nevertheless, antibiotics are considered by many a double-edged sword. Their extensive use in the past few years has given rise to a global problem: antibiotic resistance. This factor and the increasing evidence that a wide range of antibiotics can damage mammalian mitochondria, have driven a significant sector of the medical and scientific communities to advise against the use of antibiotics for purposes other to treating severe infections. Notwithstanding, a notorious number of recent studies support the use of these drugs to treat very diverse conditions, ranging from cancer to neurodegenerative or mitochondrial diseases. In this context, there is great controversy on whether the risks associated to antibiotics outweigh their promising beneficial features. The aim of this review is to provide insight in the topic, purpose for which the most relevant findings regarding antibiotic therapies have been discussed.
Suárez-Rivero JM, Pastor-Maldonado CJ, Povea-Cabello S, Álvarez-Córdoba M, Villalón-García I, Talaverón-Rey M, Suárez-Carrillo A, Munuera-Cabeza M, Sánchez-Alcázar JA. Mitochondria and Antibiotics: For Good or for Evil? Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 17;11(7):1050. doi: 10.3390/biom11071050. PMID: 34356674; PMCID: PMC8301944.
Saturday, October 22, 2022
Friday, October 21, 2022
CAN WE BOOST MITOCHONDRIAL NUMBER IN A WAY CONSISTENT WITH ORIGINAL CELLULAR TISSUE TYPE FUNCTION? THOUGHTS. 2022-10-21
IS IT POSSIBLE TO REPLACE DAMAGED MITOCHONDRIA PHARMACOLOGICALLY?
Jornayvaz FR, Shulman GI. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Essays Biochem. 2010;47:69-84. doi: 10.1042/bse0470069. PMID: 20533901; PMCID: PMC3883043.
CAN WE FACILITATE MITOGENESIS BY PROTEIN DEFICIENT FASTING? CAN WE INTRODUCE OR BOOST AMPK PRODUCTION TO STIMULATE MITOGENESIS NUMBERS CONSISTENT WITH CELL DEFICIENCY AND TISSUE SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS? CAN WE PHARMACOLOGICALLY BOOST MITOGENESIS TO PROVIDE FOR LOSSES TO ANTIBIOTICS, PESTICIDES AND COVID AND OTHER BIOCIDES? iT OCCURS TO ME WE ARE ONLY AS OLD AS OUR MITOCHONDRIA?
Thursday, October 20, 2022
Dr. Tent Gave Evidence the Autoimune Epidemic was in Fact Caused by Viruses. Commentary Resulting. 2022-10-20. Jorma Jyrkkanen
Inner Connections>Welcome to Inner Connections>Cafe>Cafe, Fun Things Archived>
The Exploding Autoimmune Epidemic - Dr. Tent - It's Not Autoimmune, you have Viruses.
Crochet Sue IC Angel
Jan 29, 2013#1
The Exploding Autoimmune Epidemic - Dr. Tent - It's Not Autoimmune, you have Viruses.
This is about vaccines, they contain viruses that cause all kinds of diseases.
I am watching this video and it is very interesting. It's 2 hrs long and I realize most do not have the time to watch it
so I'm taking notes. I was taking notes for one of my sisters, and decided to post them here too. I have only watched
a half hour so far and will post the notes I took below. I will post more as I watch it, which I won't be watching anymore
tonight, but over the next few days.
In this first half hour he is talking about the vaccines causing cancer. He hasn't talked about vaccines causing
autoimmune diseases yet. I am interested to get to that part as scleroderma, which Gabby had, is also an
autoimmune disease that starts out the same as arthritis but gets much worse when it attacks internal organs.
Quote
Share
Jan 29, 2013#2
Notes from the first half hour:
They thought a virus was the cause of cancer in the early 50's
In 1999 to 2001, 60 Minutes investigated this story and they put more money
and time into than any other story they ever aired. They said there is no way
they can air this so they didn't.
1942 antibiotics were released, 1943 polo became an epidemic. Polo mimicked
the flu so people were treated with antibiotics when they really had polo.
1955 a polo vaccine was rushed into productions. They put formaldeyde in
the vaccine. Dr. Bernice Eddy said they should test it first, she tried it on
monkeys and they were paralzed. She tried to get them to halt the vaccine
but they did it anyway. Kids got sick from polo and were paralzyed.
The polo vaccine never stopped polio, it was stopped by people practicing
better santitation and refrigeration methods.
Dr. Eddy was taken off the polio research. She and Dr. Sarah Stewart discovered
that cancer is caused by a virus.
The vaccine manufacturers were growing their polio viruses on the kidneys
of monkeys and when they removed the polio virus from the monkey kidneys
they also removed an unknown number of other monkey viruses with it.
In 1959 Dr. Bernice Eddy found overwhelming evidence that they had just
inoculated an entire generation with cancer-causing monkey viruses.
She predicted an epidemic of cancer. There is 40 monkey viruses in
the vaccines.
The government made it classified and would no longer allow information
about it out to the public.
Everyone still has these viruses from the vaccines inside of them. If you get
a blood sample analyzed they would find these viruses in it.
In 1960 Dr. Bernice Eddy gave a talk to the New York Cancer Society and announced
that she examined the monkey kidney cells in which the polio virus was grown and
found they were infected with cancer-causing viruses, SV-40.
They crushed Bernice Eddy professionally. They took away her lab, destroyed
her animals, put her under a gag order and delayed publication of her scientific
papers.
In 1961 federal regulations went into effect that required that the polio vaccines
be free of SV40 but they did NOT require the SV40 contaminated seeds used to
make every batch or lot of vaccine be discarded nor the recently manufactured
contaminated vaccines be discarded. They continued giving the contaminated
vaccines to children and adults until they were used up sometime in 1963.
In 1962 Sabin Oral Polio vaccine is introduced but they used the same culture
medium, the monkey kidneys. This was the vaccine put into the sugar cube
that everyone took back then. It is estimated that 1 out of every 200 people
are getting cancer caused by SV40.
They started to realize that cancers rarely seen such as lung, breast, prostate,
lymphoma, brain and melanoma increased 50% over a 16 year period. Lung
cancer is rising because the vaccine is causing it, not smoking. As smoking has
gone down, lung cancer has gone up.
The vaccine developers did not want to release this information. They said it
would scare the public unnecessarily. If they hear that their children were
injected with a cancer virus that would not be very good.
Men born between 1948 and 1957 have 3x as much cancer not related to smoking.
The study's researchers insist the increase cannot be explained by smoking,
better diagnosis or an agin population. Public Health Official, Devra Lee Davis
said "There's something else going on here."
The SV40 virus is also sexually transmitted and you can get it from a blood
transfusion and it is spread from mother to child even if they had never got the
vaccine shots. Those never inoculated with the contaminated vaccine inherits it
up from their parents and can pass it on or infect their children and grandchildren.
This information has been blacked out from history.
Their is also a virus in the vaccine that acts like AIDS.
Robert Gallo's group at the NCI and Litton Bionetics also experimented with other
simian and human cancer viruses (e.g., SV40), and developed recombinants (i.e. mutants)
of these with other viral nucleic acids including those that caused the prominent
features of AIDS -- WBC dysfunction, leukemias, lymphomas, sarcomas,
progressive wasting, and ultimate death in cats, mice, chickens, and humans.
All this in the likely presence of other easily mutated retrovirus contaminents.
This is what they were manufacturing.
Bisulfite induced P53 gene mutation of G:C--->A:T Probably leading to lung cancer Partial Explanation of one Cancer Increased in Pulp industry Communities. Jan 18 2013 Jorma Jyrkkanen
Bisulfite induced P53 gene mutation of G:C--->A:T Probably leading to lung cancer
Partial Explanation of one Cancer Common in pulp industry?
Jorma's News Old Story
Monica Hollstein et al. (1991) mentioned that the most common mutation in lung cancer
in the P53 gene is G:C--->A:T (found in 46% of small cell lung cancers and 57% of
non-small cell lung cancers). A reference of hers and others of interest http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2827900/.
While conducting a pulp mill air emissions health effects literature review for the Al-Pac hearings in Alberta, I found a reference to bisulfite ion ie. sulfur dioxide SO2 transforms into bisulfite ion HSO3- in T4RII Phage causing G:C--->A:T mutations (Lawrence Fishbein, 1976, Atmospheric Mutagens. 1. Suflur Oxides Plus Nitrogen Oxides. Mutation Research (32):309-330.).
Fishbein reports that bisulfite was mutagenic to viruses, bacteria and plants, and that it was a moderately strong mutagen. Low levels increased chromatid aberrations and fragments,laggards, and micronuclei were often observed. Clumping at 5 ppm inhibited mitosis. Here is a mutagen that inhibits mitosis but is linked to cancer.
Here is the Fishbein reference hidden from the poor of the world behind a $31.50 Paywall. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016511107690004X
Sulfur dioxide depressed DNA synthesis and growth and increased abnormalities in human lymphocytes [HeLa Cells]. In the mouse, Ewe, and Cow Oocytes, the alterations resulted in transmitted genetic disorders. Fragmentation, rearrangements, anaphase laggards, all led to aneuploidies {altered chromosome numbers} resulting in fetal losses and congenital abnormalities. The mammalian mutations are noteworthy and raise the flag for humans on potential similar effects.
I would suspect that these pollutants abilities do not stop here and could probably account for many more illnesses. Do we have here an almost complete environmental explanation of a genetic change leading to cancer in humans? After reading the two articles I proclaimed that bisulfite was involved in causing lung cancer. I had not seen the link made previously.
In retrospect (2013) it has been found that frank carcinogens can cause single step carcinogenesis while multiple defects and mutations are involved in cases where weaker carcinogens are involved. Because this mutation is involved in less than 100% of lung cancers bisulfite likely falls into the multiple mutation carcinogenesis. IARC lists bisulfite as a Class 3 carcinogen (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_IARC_Group_3_carcinogens). CDC does not list it (http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/cancer/npotocca.html). I was therefore wrong in proclaiming bisulfite causes cancer because it now seems more likely it is just one step in the sequence of defects leading to cancer.
The ramifications for carcinogen management and regulation are more clear however. Mutagens must be regarded as carcinogens because any one of them can be the one that causes the final mutation leading to cancer, ie the straw that breaks the camels back.
Copyright 1991 Jorma Jyrkkanen. All rights reserved.
Wednesday, October 19, 2022
The Probable Reason TREX had Small front Limbs. 2022-10-19. Jorma Jyrkkanen
It has long remained a puzzle why TREX has small front limbs.I think I know the answer.
Eggs need to be turned every day to aid in embryo development. There is no other appendage suitable but the small forelimbs and possibly the mothers tongue. We see raptors turning eggs with their bills today so we know it is a vital part of egg care. Poultry breeders Turn the eggs during incubation prevents embryo death and unhealthy hatches. Eggs must be turned at least five times every 24 hours. Turning more frequently is better and once per hour is best. Ergo small forelimbs ensure healthy Baby TREX hatches. This is my 230th Archival Blog Post.
Copyright 2022-10-19 Jorma Jyrkkanen
Monday, October 17, 2022
Physiological Adaptation in the Neoproterozoic to Early Cambrian to Dynamic Oxygen Fluctuation Challenges Enabled Respiratory Evolution. Oct 2022 Jorma Jyrkkanen
Christopher Clifford
33m ·
Dynamic Oxygen Levels May Have Accelerated Animal Evolution:
"The question scientists have tried to answer is - was there anything extraordinary about the changes to oxygen levels in the Neoproterozoic Era that may have played a pivotal role in the early evolution of animals – did oxygen levels suddenly rise or was there a gradual increase?
Dr Benjamin Mills, who leads the Earth Evolution Modelling Group at Leeds and supervised the project, said: “This periodic change in environmental conditions would have produced evolutionary pressures where some life forms may have become extinct and new ones could emerge.”
“When oxygen levels decline, there is severe environmental pressure on some organisms which could drive extinctions. And when the oxygen-rich waters expand, the new space allows the survivors to rise to ecological dominance.
“These expanded habitable spaces would have lasted for millions of years, giving plenty of time for ecosystems to develop.”
Extreme variability in atmospheric oxygen levels in the late Precambrian
Alexander J. Krause https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9771-8101 , Benjamin J. W. Mills https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9141-0931, Andrew S. Merdith https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7564-8149, Timothy M. Lenton https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6725-7498, and Simon W. Poulton https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7621-189X
Science Advances 14 Oct 2022 Vol 8, Issue 41
Abstract
Mapping the history of atmospheric O2 during the late Precambrian is vital for evaluating potential links to animal evolution. Ancient O2 levels are often inferred from geochemical analyses of marine sediments, leading to the assumption that the Earth experienced a stepwise increase in atmospheric O2 during the Neoproterozoic. However, the nature of this hypothesized oxygenation event remains unknown, with suggestions of a more dynamic O2 history in the oceans and major uncertainty over any direct connection between the marine realm and atmospheric O2. Here, we present a continuous quantitative reconstruction of atmospheric O2 over the past 1.5 billion years using an isotope mass balance approach that combines bulk geochemistry and tectonic recycling rate calculations. We predict that atmospheric O2 levels during the Neoproterozoic oscillated between ~1 and ~50% of the present atmospheric level. We conclude that there was no simple unidirectional rise in atmospheric O2 during the Neoproterozoic, and the first animals evolved against a backdrop of extreme O2 variability.
Mechanisms of Adaptation
Jorma Jyrkkanen
Blood stem cells today in mammals have the ability to produce more when challenged by oxygen deficit. Secondary polycythemia most often develops as a response to chronic hypoxemia, which triggers increased production of erythropoietin by the kidneys. This kind of condition may have early antecedents in the Neoproterozoic facilitating adaptation to hypoxia challenge and enabling higher respiratory processes to evolve. Looking for evidence of this capability in more primitive phyla might yield important clues to what exactly happened to improve respiratory adaptation. I suspect mitochondria also improved during this time. Oxygen is central to aerobic respiration—it is the terminal electron acceptor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), which transfers electrons from high energy metabolites through a series of carriers to drive ATP generation from ADP. The ability to increase mitochondria in hypoxia challenge may have also facilitated Neoproterozoic respiratory adaptation. These oxygen fluctuations would have created ideal situations for aerobic glycolysis, anaerobic glycolysis, and pyruvate fed xidative phosphorylation metabolisms at various times not to mention ideal situations for alternate metabolisms like methane and CO2 drives. Cancer cells today operate optimally on glycolysis suggesting they may have originated in this dynamic gas fluctuation era.
Friday, October 14, 2022
We Were Made Possible by a Symbiotic Fusion of Two Prokaryotes about 1.8-2 bya Like Plants Which Also Acquired Phtosynthetic Endosymbionts. 2022-10-14 Jorma Jyrkkanen
ORIGIN OF MITOCHONDRIAMitochondria originated by permanent enslavement of purple non-sulphur bacteria. These endosymbionts became organelles through the origin of complex protein-import machinery and insertion into their inner membranes of protein carriers for extracting energy for the host. Mitochondria originated by permanent enslavement of purple non-sulphur bacteria. These endosymbionts became organelles through the origin of complex protein-import machinery and insertion into their inner membranes of protein carriers for extracting energy for the host.
THE PROKARYOTE MICROBES THAT ENGULFED PURPLE NON-SULPHUR BACTERIA Archaea were the most likely candidate. In particular, The origin of eukaryotes remains unclear1,2,3,4. Current data suggest that eukaryotes may have emerged from an archaeal lineage known as ‘Asgard’ archaea5,6 (Isolation of an archaeon at the prokaryote–eukaryote interface. Hiroyuki Imachi, Masaru K. Nobu. 15 January 2020)
EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THIS THEORY OF THE EARLY ORIGIN OF HIGHER LIFE(Organismal Biology)
Mitochondria (and chloroplasts) are approximately the same size as prokaryotic cells, but they are located inside much much larger eukaryotic cells instead of free-living.
Mitochondria (and chloroplasts) each have their own DNA, their DNA is organized in a circular chromosome like typical prokaryotic genomes, and their genomes contain genes that are very similar to genes found in prokaryotic genomes.
Mitochondria (and chloroplasts) reproduce by binary fission, the process that prokaryotes use to reproduce. In contrast, eukaryotic cells reproduce by mitosis.
If the mitochondria (or chloroplasts) are removed from a eukaryotic cell, the cell has no way to produce new ones. In other words, the “instructions” to make new mitochondria/chloroplasts is not present in the eukaryotic nuclear genome; they are present in the mitochondria/chloroplast genomes.
The membrane composition of mitochondria (and chloroplasts) is more similar in composition to prokaryotic membranes than to eukaryotic membranes.
Thursday, October 13, 2022
Impact of Antibiotics on Mitochondria Increase Risks of Cancer, Heart Disease, Failed Immune system and Other Medical Problems. JCCM 2 Oct 2020. Jorma Jyrkkanen.
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 163https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
Research Article
Antibiotic induced changes to
mitochondria result in potential
contributions to carcinogenesis,
heart pathologies, other medical
conditions and ecosystem risks
Jorma Jyrkkanen*
British Columbia, Canada
More Information
*Address for Correspondence: Jorma
Jyrkkanen, British Columbia, Canada,
Tel:1-250-859-5330;
Email: jormabio@hotmail.com
Submitted: 17 August 2020
Approved: 01 October 2020
Published: 02 October 2020
How to cite this article: Jyrkkanen J. Antibiotic
induced changes to mitochondria result in
potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart
pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks. J Cardiol Cardiovasc Med.
2020; 5: 163-171.
DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
Copyright: © 2020 Jyrkkanen J. This is an open
access article distributed under the Creative
Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction
in any medium, provided the original work is
properly cited.
Keywords: Antibiotic; Mitochondria; DNA
damage; P53 tumor suppressor cene; Mutp53;
ROS; Lipid peroxide; Cell perforation; Cell
rupture; Oxidative phosphorylation; Cancer;
Carcinogenesis; Glycolysis; Warburg effect;
Microbiome; Dysbiosis; Immune suppression;
Pesticides; Mechanism; Clastogenic; Epigenetic
silencing; Microrna; DNA; Heart
OPEN ACCESS
Abstract
With the discovery by Calghatgi (2013) that three common antibiotics (Abs) increased
mitochondrial reactive oxygen (ROS) and lipid peroxide (LP) and depleted their natural absorbant
glutathione led me to investigate further the potential impacts of these genotoxic substances on
carcinogenesis. The range of impacts on mitochondria and cellular DNA varied by antibiotic to
those consistent with known prior contributions to carcinogenesis. Specific cancers probably
increased by these changes were HCC, RCC (KCC), CRC, cancer of the esophagus. Tumor
suppressor gene mutations resulting from LP were noteworthy in this regard and mutations induced
in CRC were consistent with those found in carcinogenesis of CRC. In addition depression of
short chain fatty acids in microbiomes were found which depress the immune system increasing
risk of all cancers. Many cancers were increased according to epidemiological studies linking
Abs with elevated odds ratios, with one concern in particular, fatal breast cancer. The impact of
loss of functionality of the mitochondria was also linked to depression of the citric acid cycle and
therefore ATP which deflected metabolism to glycolysis, the Warburg mechanism also increasing
risk of all cancers, favoured by cancer cells. In conclusion, some portion of many cancer types
are probably increased in likelihood by number, type and frequency of Abs treatment and chronic
residue exposure which varies from individual to individual. This led me to propose a three
pronged carcinogenesis mechanism for Abs. 1. Cancer critical mutations 2. Immune depression
3. loss of mitochondrial functionality leading to Warburg effects. Damage to mitochondria were
also noted by common pesticides tested in China and cancer associations were also found for
many pesticides supporting a similar contributory etiology. Heart health concerns were raised by
these findings because of the myriad mitochondria in the heart and because of long term reliability
needs. Studies suggesting hearts were affected by Abs and pesticide exposure were presented.
Because of their geographical ubiquitousness and the huge range of diseases associated with
mitochondrial dysfunction, antibiotics and pesticides and bacteriocidal biocides are of concern
for biodiversity and life in general. I propose research steps to evaluate Abs safety and suggest
directions for further research and make suggestions on ways to ameliorate Abs toxicity.
Introduction
Antibiotics kill or slow the growth of bacteria or interfere
in their reproduction. The mitochondria, an ancient alpha-
proteobacteria [Rickettseae] that has become an endosymbiont
in higher life forms with critical functions, response to them
has been found to be a decrease of beneβicial antioxidant
glutathione, increased reactive oxygen, increased harmful
lipid peroxide, possible DNA damage and mutations in tumour
suppressor genes increasing cancer risk, possible inability to
reproduce, possible cell perforation and or rupture. Some
antibiotics have been shown in the past to be clastogenic.
These types of responses have broad biochemical and health
implications. They could lead to carcinogenisis, microbiome
dysbiosis with resulting immune system depression and or
loss of oxidative phosphorylation (OP) favouring glycolysis
metabolism which is also the favoured method for cancer
cells. Changes could enhance the Warburg effect favouring
cancers. P53 genes may be turned off epigenetically at the
DNA. Defective mitochondria have been implicated in over
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 164https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
200 medical conditions. In addition a big unknown is the
relationship between which biocides may epigenetically shut
down critical genes found with each particular kind of cancer.
Clinical and epidemiological evidence supports the conclusion
that some antibiotics are carcinogens, others promote cancers
and cancer risk increases with frequency and type. Microbiome
dysbiosis and immune depression risk is increased. While
exposure may not complete all the steps to cancer it may
contribute important mutations along the way. Other life time
exposures can can complete the process. Chinese researchers
recently found that a high proportion of common pesticides
ruptured mitochondria like some antibiotics. Individuals who
were exposed to pesticides were more than twice as likely
overall to have conditions like heart disease, heart failure or
an irregular rapid heartbeat known as atrial βibrillation [1]. It
can be inferred that ruptured mitochondria from antibiotics
would lead to similar coronary pathologies. There is reason
to suspect that all Eukaryotes are subject to pathological
impacts. The mitochondria enabled multicellular evolution
to higher forms of life and is now under attack worldwide
by anthropogenic biocide pollution. More research is needed
to determine which of all biocides is mitochondria friendly,
enables them to be fully functional without mutations, prior
to regulatory approvals. I propose an antibiotic mitochondria
carcinogenesis mechanism. For a general overview of impacts
of antibiotics on total general physiology and health of
ecosystems including plants see Wang, Xu et al. [2]. A criticism
of some βindings is that people with cancer are more prone
to infections and this can account for much of the association
of antibiotics with cancer [3]. However the βinding of immune
compromise is consistent with antibiotic induced microbiome
associated dysbiosis.
Mitochondrial job and creation of toxic mix by antibiotic
Mitochondria, a primitive endosymbiotic bacteria, related
to extant SARII marine bacteria and Rickettsias, in eukaryotes
is responsible for OP resulting in ATP and NAD production
for energy. When exposed to clinically equivalent doses
of antibiotics that target bacteria (cipromycin, ampicillin,
kanamycin), exhibited a decline in glutathione titre, an
increase in reactive oxygen (ROS) and an increase in lipid
peroxide with damage to DNA and potential mitochondrial
rupture [4]. Tetracyclines used for humans and livestock have
also been linked to mitochondrial genetic damage [5]. Some
antibiotics have been found to be break chromosomes [6].
Modes of action of antibiotics on mitochondria and
microbiome
1. quinolones- commonly prescribed antibacterial
organoβluorine compounds which act by inhibition of
bacterial DNA synthesis and result in rapid cell death [7]. This
group contains oβloxacin, norβloxacin (noroxin), ciproβloxacin
(Cipro), moxyβloxacin (Avelox). Expectation is to obstruct
mitochondrial replication. Norβloxacin demonstrated a linear
antibiotic-DNA mutation rate, compromised DNA oxidative
damage repair and post replicative mismatch repair [8].
They could be expected to do similar collateral damage to
mitochondria and to members of the human microbiome.
2. aminoglycosides-ex gentamicin, amicasin which
create holes in the outer cell wall of bacteria suggesting
mitochondria and the microbiome might be at risk of similar
damage [9]. Damage to lipid membranes can be expected.
Lipid membranes have wide distribution in both microbes
and other animals including humans.
3. β-lactams or penicillin derivatives such as
cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems, carbacephems
inhibit cell wall synthesis in bacteria and by inference inhibit
cell wall synthesis in mitochondria during division and repair
and microbiomes thereby obstructing microbial reproduction.
Penicillamine is listed as a ‘developmental’ in California
Proposition 65.
4. Tetracyclines-used on cattle and humans and
possibly acquired secondarily as dietary residues may affect
mitochondria because they speciβically target Rickettsias a
probable evolutionary ancestor [2,10.11].
5. Anthracyclines-result in clastogenicity [6].
Harmful impact of liberated substances on DNA, P53
tumour suppressor gene, mutagenicity and known
effects in other cancers
Glutathione is an antioxidant that soaks up ROS and is
essential for many neurological and other body functions.
Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important
cellular components caused by reactive oxygen species such
as free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals.
Genomic instability occurs in myeloid malignancies with
increased reactive oxygen species ROS, DNA double strand
breaks (DSBs) and error-prone repair [12].
ROS linked to many cancers by oxidative DNA damage
“numerous studies have shown generation of reactive
oxygen species (ROS) that can cause oxidative damage of DNA.
This is a well-known mechanism in carcinogenesis for many
agents” [13].
Excessive levels of ROS accumulation due to altered
equilibrium between ROS and antioxidants may lead to
different kinds of diseases such as atherosclerosis, diabetes,
neurodegeneration, and cancer including CRC. It is widely
known that ROS-induced DNA damages and genetic mutations
are critical causes of cancers including CRC. The main
intracellular DNA lesions caused by ROS are single and double
strand DNA breaks, and the common genetic mutations
include p53, KRAS, APC, and BRAF mutations often seen in
CRC’s. For example, a direct relation among oxidative stress,
DNA damage and elevated frequency of p53 mutation in CRC
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 165https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
has been observed. Most extensively studied endogenous
DNA damage by ROS is the formation of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-
2’-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG). As the biomarker of oxidative
stress, 8-oxodG level is higher in colorectal tumors than in
normal mucosa. Mitochondrial DNA is particularly prone to
be oxidatively damaged and is more meaningful in colorectal
carcinogenesis [14].
I would expect antibiotic induced drop in antioxidant
glutathione to contribute to such an altered equilibrium and
assay for 8-oxodG post antibiotic treatment might be a good
indicator of antibiotic carcinogenic potential as well as looking
for deβicits of ATP, an indicator that metabolism has switched
to cancer cell loving glycolysis from pyruvate metabolism.
Lipid peroxide associated cancers
Besides being generated by mitochondria exposed to
antibiotics, lipid peroxide is also increased with analgesics
like aspirin (though some studies show it reduces LP) and
NSAIDS naproxin, indomethacin and diclofenac, being male,
among hypertensives, diabetics, smokers, oophorectomized
and pregnant women especially with eclampsia and pre-
eclampsia [15]. Ochratoxin a mycotoxin found in cereals and
grains also increases LP. These mutiple sources need assaying
when making links to antibiotics impact on mitochondria.
Lipid peroxide has been linked to esophageal
carcinogenesis [16] and to red meat and treated meat colon
carcinogenesis [17]. The major lipid peroxidation product,
trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, preferentially forms DNA adducts
at codon 249 of human p53 gene, a unique mutational hotspot
in hepatocellular carcinoma [18]. In a seemingly unrelated
exposure from aβltoxin researchers report an increased
frequency of loss of the Hae III allele and base G mutation on
p53 gene at codon 249 where it is mutated to C [19]. Why this
matters is because this same P53 gene locus is linked to HPV
cervical cancers from a study done on Kenyan women [20].
HPV cancers are associated with genital, anal and oral tissues.
Antibiotics production of lipid peroxide and its metabolites
can also mutate this gene locus and that is found with HCC.
Lipid peroxidation has been proposed as a mechanism for
renal cell carcinoma RCC [15]. Based on their work I added my
comments. Lipid peroxide (LP) degrades into mutagens that
target tumor suppressor gene p53 and may alter functionality
of other tumor suppressor genes like VHL speciβically linked
to hereditary RCC and is postulated by me and the latter
authors to be a carcinogen linked to renal cell carcinoma.
I phrase this as a question. Lipid peroxide is generated by
antibiotics attacking mitochondria which then release it into
the tissue environment and may even rupture cells in the
process. I recommend an investigation to study additionally
antibiotic history in regards to VHL depressed kidney cancer.
The placenta is the main source of LP in pregnant women.
Look also at Aspergillis and ochratoxin A as a mutagen for the
TSG genes involved. The following article hints at LP causality.
Fumonisims, a fungus in corn and other grains is linked to
kidney cancer and is possibly acting through mutation of
the p53 gene. P53 overexpression has been correlated with
increased RCC. Inactivation of the VHL TSG is responsible
for polycystic kidney disease and for renal cell carcinoma of
the hereditary VHL cancer syndrome and for the majority of
sporadic renal cell carcinomas.
Protectively, polyphenolics in red wine are postulated to
soak up the lipid peroxides and reduce RCC risk. Estrogens
especially 2-hydroxyestradiol, mannitol, SOD and vitamin E
are all LP sponges along with the mitochondrial glutathione.
This suggests antibiotics are a cofactor in carcinogenesis
of several if not multiple cancers via this same p53 locus 249
mutation’s contribution or by lipid peroxide contribution and
ROS contributions to reduce TSG DNA repair and function.
Lipid peroxide metabolite hydroxy-2-nonenal is also found in
red meat and treated meat carcinogenesis. It is safe to conclude
that antibiotics are one cause of or major contributing factor
to hepatocelluar carcinoma and are also potentially involved
in colon carcinogenesis. In CRC, the commonest lipid
peroxidation products are MDA and HNE, the levels of which
in the CRC tissue are signiβicantly increased with clinical
staging [21]. CRC and RCC are likely to be cancers potentially
associated with antibiotic mitochondrial disruption.
P53 changes associated with warburg effect
Possible P53 gene upregulation (PUMA->WTP53) may
lead to the Warburg effect favouring cancer [22]. Proximicins
A, B, and C—antitumor furan analogues of netropsin from the
Marine Actinomycete verrucosispora induce upregulation of
p53 though I am not certain this is the same effect as PUMA
[23]. Mutated P53 actually becomes the mutP53 guardian of
cancer cells [24].
Normal function of p53 blocked by loss of mitochondria
through damage or rupture
Tumor suppressor p53 plays a central role in tumor
prevention. As a transcription factor, p53 mainly exerts its
function in tumor suppression through its transcriptional
regulation of its target genes to initiate various cellular
responses.
Cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and senescence are most well-
understood functions of p53, and are traditionally accepted as
the major mechanisms for p53 in tumor suppression. Recent
studies have revealed a novel function of p53 in regulation of
cellular metabolism. p53 regulates mitochondrial oxidative
phosphorylation, glycolysis, glutamine metabolism, lipid
metabolism, and antioxidant defense. Through the regulation
of these metabolic processes, p53 maintains the homeostasis
of cellular metabolism and redox balance in cells, which
contributes signiβicantly to the role of p53 as a tumor
suppressor [25].
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 166https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
P53 Cell guardianship and critical OP obviously cannot
happen if the mitochondria is ruptured or defective or if
the p53 gene has been mutated, silenced or sequestered to
assist cancer cells. With diminished OP, Warburg effects will
increase and cancer cells will be given a boost. This might well
be a serious collateral impact of antibiotics.
Antibiotics render the immune system less effective in
infection
Researchers reporting in Frontiers in Microbiology found
that short chain fatty acids (SCFA) from resident bacteria were
important in protecting the immune system, and inβlammation
control. Both of these side effects have important ramiβications
for prevention of cancer initiation. Antibiotics diminished
resident bacteria carrying out this role and supplemental
SCFA were not effective in ameliorating the effect.
Dysbiosis of resident microbes is unequivocally
associated with immune-related disorders and opportunistic
and pathogenic infections which can themselves set the
stage for cancer [26]. If potentially carcinogenic microbes
Helicobacter pylori, Streptococcus bovis, Salmonella typhae,
Fusobacterium, Chlamydophyla, Bartonella or Caries bacteria
or any carcinogenic viruses such as EBV, HPV, alpha-HPV,
beta-HPV, HHV, HBV, HVC, KSHV and possibly retroviruses
or Schistosomes and liver βlukes facilitated by [27] depressed
immune systems proliferate as a consequence this can lead
to increased incidence of cancers especially the viral cancers
which do not respond to antibiotics but will take advantage of
a depressed immune system.
Along this line there has been an increase in oropharyngeal
HPV cancers in Canadian men [28]. The depressed immune
system may also lessen the bodies ability to kill cancerous
cells regardless of their etiological origins. Another of the
consequences of antibiotic use is development of antibiotic
resistance. One of the carcinogenic bacteria, H. Pylori is
an example [29] the consequence of which may lead to an
increase in stomach cancers in developed countries unless we
can come up with new more effective mitochondria friendly
antibiotics.
The evidence of carcinogenesis from research
Seeing that these changes were consistent with steps
found in carcinogenesis [30] I asked the question, what is the
clinical and epidemiological evidence that antibiotics increase
the risk of cancer? It appears others have also addressed this
question [31,32], [antibiotic use predicts an increase in the
risk of cancer]; I reproduce Kilkkinen’s results because they
speak to the range of cancers brought under suspicion.
“The use of antibiotics was associated with an increased
risk of cancer; for categories of increasing antibiotic use (0–1,
2–5 and #6 prescriptions), RRs (95% CIs) were 1.0 (reference),
1.27 (1.26–1.29) and 1.37 (1.34–1.40). The association was
found both in men (RR for comparison of lowest and highest
exposure group 1.47, 95% CI 1.42–1.53) and women (RR 1.31,
95% CI 1.28–1.35). The most common cancers i.e. prostate,
breast, lung and colon comprised half of all cancer cases; RR
(95% CI) was 1.39 (1.31–1.48) for prostate, 1.14 (1.09–1.20)
for breast, 1.79 (1.67–1.92) for lung, and 1.15 (1.04–1.26)
for colon cancer. RRs for other primary sites varied between
0.90 (0.76–1.05) for ovary and 2.60 (1.60–4.20) for endocrine
gland cancers. In addition to endocrine gland and liver
cancers, the risk of non-melanoma skin, duodenum, pancreas,
kidney, bladder, male genitals (excluding prostate) and
thyroid cancers as well as myeloma and leukemia was more
than 1.5 times higher among participants with 6 or more
antibiotic prescriptions compared with the lowest exposure
group. Restricting analyses to participants with 5 or more
years follow-up did not produce signiβicantly different results
from those covering the entire study population (RR for the
comparison of lowest and highest exposure group 1.37, 95%
CI 1.34–1.40). Similar results were obtained when the data
were stratiβied according to age (data not shown). We also
observed an increased risk of death due to cancer with use of
antibiotics (RR 1.33, 95% CI 1.28–1.38). There was a similar
tendency for an increased cancer risk with annual antibiotic
use (table is available from authors by request). Compared
with non-users of antibiotics, RRs (95% CI) for 1 year,2 and 3
years of use were 1.33 (95% CI 1.32–1.35), 1.40 (1.38–1.42)
and 1.46 (1.43–1.49), respectively. RRs (95% CI) for 3 years
of use for different primary sites varied from 0.99 (0.86–1.14)
for ovary to 1.81 (95% CI 1.62–2.02) for non-melanoma skin
cancers and was 1.21 (1.15–1.26) for breast and 1.57 (1.49–
1.66) for prostate cancers.”
Tim Newman 2017 [33] [antibiotics may increase
the risk of bowel cancer]; Millipore-Sigma 516104 [34].
[penicillin/streptomycin/amphotericin-harmful, teratogenic
and carcinogenic]). Velicer et al. [35] found prolonged use
of antibiotic increased risk of fatal breast cancer. This has
broad global ramiβications because of the chronic long term
exposure of antibiotic residues in diet from treated foods such
as beef, pork, poultry and farmed βish and sea food products.
In a new epidemiological study ‘intakes of dairy calories and
dairy milk were associated with BC hazard ratios (HRs) of
1.22 [95% conβidence interval (CI): 1.05–1.40] and 1.50 (95%
CI 1.22–1.84)’ [36].
These results are deeply troubling despite any
experimental difβiculties because they almost unanimously
point in the same direction to increasing carcinogenicity and
the huge global populations exposed to residues. Zhang et al.
[3] offered criticisms of association studies and the reader is
encouraged to weigh them against the evidence presented
here. My rebuttle is that the above βindings are also consistent
with reactive oxygen DNA adduct mutations’ range of cancers,
defective tumor suppressor genes and Warburg effects
from mitochondrial OP knockdown and antibiotic induced
dysbiosis induced immune compromise.
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 167https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
IARC anomaly discussion
The problem in developed countries is that use a lot of
antibiotics is that infection related cancers are lower than
in the Third World [cf. 7.4% versus 22.9%] showing that
they are protective for these but overall reported in 2019 in
Canada for example is that cancer incidence reported is 50%
[37]. This suggests carcinogen and life style related cancers
(see Proposition 65 list) and perhaps population of age classes
contribute to the high rate. This anomaly suggests cumulative
mutations and other mechanisms such as I am investigating
and exposures are setting the stage for later cancer illness.
That we have long insidious exposure to mutation inducing
carcinogens and endocrine disruptors is conβirmed by my
review of pesticide and chemical carcinogens in mothers
breast milk [38].
CRC cancers increasing in Canada
How safe and contributory to cancer are antibiotics?
This can be addressed considerably by the experiments I
propose at the end of this article. Colorectal cancers (CRC)
are very informative in this story. CRC incidence increased
exclusively in young adults in nine high-income countries
spanning three continents, potentially signalling changes in
early-life exposures that inβluence large bowel carcinogenesis
[39] and a fail for antibiotics for this cancer and microbiome
dysbiosis may play a pivotal role. Another intriguing
possibility is inherited epigenetic markers from parental
exposures. Alcohol and obesity are confounding factors for
CRC etiology with interaction effects [40]. Downregulation
of tumor suppressor gene TUSC3 facilitates proliferation of
colon cancer CRC. Its absence or dysfunction of expression
after exposure to chemicals and drugs can give a prognosis of
chemicals safety [41].
Antibiotics change tissue environment to favour cancer
metabolism by the warburg effect
In addition, one of the antibiotics classes tested was linked
to a decline in pyruvate, the feed stock for the citric acid cycle
and ATP and NAD production or OP. With the loss or reduction
of OP the default respiration glycolysis increases dominance.
This is called the Warburg Effect which cancer cells have
been shown to prefer in which they employ glycolysis instead
of OP for their energy and this may result from defects in
mitochondria(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warburg_
effect_(oncology)).
It can be expected that this ideal environment for
glycolysis favouring cancer cells will be the norm whenever
and wherever mitochondria are damaged or ruptured as they
are with these antibiotics tested and with common pesticides
and if pyruvate is speciβically diminished.
Increasing mitochondrial reproduction should reverse
this process by restoring OP, replacing the Warburg effect,
and that is exactly what is found [42]. This βinding is strong
conβirmation of the carcinogenic effect of losing mitochondria
and their function. Aerobic exercise suggests itself to me as a
way to build up mitochondria and βight carcinogenesis via this
mechanism.
My Proposed Antibiotic Mitochondrial Carcinogenicity
Mechanism AMCM
Requirements for carcinogenesis contribution
Induce mitochondrial malfunction, damage or rupture-YES;
prevent mitochondria from faithful reproduction in quality
and quantity-Probable; cause mutations and genetic material
damage-YES; interfere with tumour suppressor genes-YES;
create microbiome dysbiosis-YES; harm the immune system-
YES; increase the Warburg effect-YES; statistically signiβicant
associations-Probable.
AMCM
1. Reactive oxygen linked to oxidative mutations of DNA
found in many cancers and Lipid peroxide induces P53
mutations and mutated P53 no longer repairs DNA and may
in fact assist cancer cells and probably the primary cause of
some portion of hepatocelluar carcinomas
2. Glutathione deβiciency increases toxicity of many
metabolites it normally neutralizes
3. Obstruct mitochondrial and microbiome lipid
membrane integrity and mitochondrial replication leading to
OP reduction and increasing microbiome dysbiosis
4. Reduction of OP and mutant P53 increase Warburg Effect
favouring cancer cells glycolysis providing an advantage to
cancer cells
5. Antibiotic induced microbiome dysbiosis immune
compromise decreasing efβicacy of subjects cancer immune
defense mechanisms
Further research suggested by these studies includes
testing all antibiotics for their mitochondrial impacts.
Related mitochondrial stressors and potential ramifica-
tions
These βindings also raise the question are there pesticides
with similar consequences? There are intriguing βindings in
China. 9 Common pesticides tested induce morphological
changes of mitochondria at low concentrations. Paraquat,
rotenone, chlorpyrifos, pendimethalin, endosulfan,
fenpyroximate and tebufenpyrad induced mitochondria
fragmentation. Furthermore, some of them (paraquat,
rotenone, chlorpyrifos, fenpyroximate and tebufenpyrad)
caused a signiβicant dose-dependent decrease of intracellular
ATP suggesting increased risk of Warburg syndrome because
ATP is a proxy for OP integrity. Interestingly, these pesticides
which induce mitochondria dysfunction also inhibit 26S
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 168https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
and 20S proteasome activity [43] which suggests to me we
should be looking at antibiotics and proteasome homeostasis
because of its required integrity for health. These results in
turn raise the obvious question, are the consequences similar
in terms of potential long term carcinogenicity? The answer
is yes [44] in which they state that “Chemicals in every major
functional class of pesticides including insecticides, herbicide,
fungicides, and fumigants have been observed to have
signiβicant associations with an array of cancer sites”.
Biocide-mitochondrial effects on heart function
Another interesting question. The heart muscle is full of
mitochondria. Do antibiotics and pesticides affect the hearts
mitochondria and if so in what way and for how long? I
would expect this heart loss of OP combined with ROS and
increased peroxides to lead to a condition like chronic fatigue
and possibly compromised coronary function. Azithromycin
induced increased deaths in patients with prior coronary
issues according to study authors Wayne A. Ray, Ph.D. and
C. Michael Stein, M.B., Ch.B., and Dan May 17 May 2012. John
R. Giudicessi et al. 2013 [45,46] also found increased risk of
sudden death from Azithromycin. Azithromycin is a macrolide
which prevents bacteria from growing by interfering
with their protein synthesis. How this might be linked to
mitochondrial protein production needs to be examined.
A UBC study found a 2.4 X increased risk of mitral valve
regurgitation in βluoroquinolone users [47]. This is an area
needing more research and review. FDA [48] issued a warning
that some antibiotics used for URI’s and urinary infections
can cause aortic rupture and prescriptions to people at risk is
contraindicated.
Lifetime cumulative augmentation
Cumulative antibiotic for clinical treatment exposures are
unwittingly augmented by chronic low level residues of other
antibiotics from dietary sources like poultry, beef, farmed βish
and pork and may not immediately cause a cancer but may
contribute to the conditions for one to occur at a later date
by facilitating entry of carcinogenic infectious agents. Other
mutagens and carcinogen residues (See California Proposition
65 List), radiation, chemical and pesticide residues and
immune decline with age can complete the cancer induction.
Calghatgi (1973) suggests that deleterious effects of
bactericidal antibiotics were alleviated in cell culture and
in mice by the administration of the antioxidant N-acetyl-l-
cysteine or prevented by preferential use of bacteriostatic
antibiotics. Is this sufβicient to eliminate the microbiome
dysbiosis immune depression effects and does it work for all
antibiotics including tetracycline which speciβically targets
relatives of mitochondria in humans? This needs critical
examination because of the enormous populations exposed.
An evolution approach enables these extrapolations
These βindings in normal mitochondria of their stress
response to antibiotic biocides is consistent with their
evolutionary origin from Rickettseae alpha-proteobacteria
and are linked to biochemical pathways already shown
linked to carcinogenesis and conβirmed in the literature.
Another probably most deβinitive path to investigate the
carcinogenicity of antibiotics is to run epigenetic proβiles on
them to determine of they are able to turnoff genes found
turned off in DNA and microRNA in cancers [49,50]. Each
antibiotic and mitochondria rupturing pesticide should be put
through trials to look for P53 upregulation, mutation (mutP53)
and epigenetic silencing in mice and rats at ppb resolutions.
Calghatgi tests should be included on all antibiotics and
pesticides that rupture mitochondria at ppb resolutions as
well as testing for missense mutations, characteristic of p53
mutations associated with carcinogenesis [51] and of course
the CRC risk indicator assay pre and post antibiotic treatment
for [8-oxodG] titre. A simple test to determine Warburg
potential would be to compare pre and post antibiotic
treatment intracellular ATP titre. Uncontacted Tribes with
infection linked cancers might also be good controls for p53
mutations, p53 upregulations, p53 epigenetic silencings but
some of them would of course have been exposed to plants
that have traditional medical effects [52] and their sample
size would be small. Another potential cell guardian to
assess for antibiotic related mutations, epigenetic silencing
is the suspected tumor suppressor trichoplein/mitostatin
(TpMs) which inhibits mitofusin-2 and hence mitochondrial
associated membrane formation, but is downregulated or
mutated in a number of types of cancer [53].
Challange to my fundamental thesis, Wallace 2012 [54]
Wallace opens with cancer needs functional mitochondria
to prosper. This seems to imply disaster for my above
hypothesis. However in further reading I βind his conclusions
strongly supportive. My response to his work is this. How do
his βindings speak to my antibiotic-mitochondrial knockdown-
cancer hypothesis? The glutathione, ROS, lipid peroxide DNA
mutagenicity, microbiome dysbiosis are part of my answer.
He also [supportively] states “mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species (ROS).......altering the activities of transcription factors
such as HIF1α and FOS–JUN to change gene expression and
stimulate cancer cell proliferation.” Moreover he adds “Cancer
cell ROS production inactivates caveolin 1 in adjacent stromal
βibroblasts. This increases mitophagy, reduces mitochondrial
function and increases lactate production in these βibroblasts.
Secreted stromal cell lactate then fuels cancer cell oxidative
metabolism, which drives tumour growth and proliferation.
This is known as the ‘reverse Warburg effect’. Its clear that
one analysis needed to determine antibiotic/biocide/selected
pesticide carcinogenicity is to measure the cancer cells
mitochondrial ROS and lipid peroxide output in response to
biocide use. I expect cancer cell mitochondria to respond the
same as normal cellular mitochondria with low glutathione,
increased ROS and lipid peroxide. This is an easy test. A careful
read shows his work is supportive of my hypothesis.
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 169https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
Follow up research
To resolve the safety of antibiotics (Abs) regarding their
potential impact on mitochondrial impacts, I have arrived
a number of research questions which can help steer our
understanding and antibiotic futures. Independent academic
institutional involvement is preferred so that vested interests
don’t cloud the results.
1. How large and persistent is the glutathione decrease,
ROS and lipid peroxide increase post antibiotic treatment for
each antibiotic if any?
2. What effect do Abs have on future reproduction, integrity
and populations of mitochondria in heart muscle.
3. Need to survey and list genetic mutations and epigenetic
alteration of cancer gene expression and especially cancer
gene silencing post Abs treatment in DNA and microRNA.
4. Assess dysbiosis linked impacts on immune system post
Abs treatment and duration of the effect.
5. Do a full analysis of coronary function and mitochondrial
health post Abs for each Abs.
6. Broad survey of Abs clastogenicity with complete
description.
7. Which Abs rupture mitochondria and or cells and at
what concentrations?
8. Assay 8-oxodG post Abs treatment to determine
potential carcinogenicity?
9. Do any Abs impact on promotion of hepatocellular
carcinoma and CRC?
10. Assay tumor suppressor epigenetic gene up-regulation,
down-regulation, silencings and mutations and their loci for
P53 and TUSC and TpMs.
11. Conduct a population study for Abs usage and Breast
Cancer with proper controls and examine BC associated
genes [55] for mutations or epigenetic silencings post Abs
treatments and relationship to exposure history.
12. Assess OP and glycolysis potential of each Abs to
determine potential for Warburg effect.
13. Abs history study of HPV oropharyngeal cancers in
men in developed countries.
14. Abs impact on proteasome activity.
15. Assay Abs for reverse Warburg activity for H1F(alpha)
and FOS-JUN which stimulate cancer cell proliferation.
16. Assay Abs treatment for caveolin 1 in adjacent stromal
βibroblasts which increase mitophagy and lactate in βibroblasts
driving tumor growth and proliferation.
17. Routine clinical assay for interstitial ATP titre recovery
once antibiotic use is discontinued to see if the Warburg effect
if initiated on application has been neutralized.
I think this would clarify the scale and degree of impact of
antibiotics and point to areas needing remedies. Many other
diseases are linked to mitochondrial alterations. The reader
is referred to Salvatore diMauro and Darryl C De Vivo book
Diseases of Mitochondrial Metabolism. Basic Neurochemistry:
Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition. Siegel
GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, et al. [39], editors. Philadelphia:
Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Salvatore diMauro and Darryl C De
Vivo.
The most urgent in the light of growing antibiotic resistance
are these two critical health questions, ie mitochondrial health
relative to heart health and carcinogenicity contributions.
References
1. Lisa Rapaport. 2019. Health News January 9, 2019 / 3:30 PM/Reuters.
2. Wang X, Dongreol R, Johan A. Antibiotic use and abuse: A threat to
mitochondria and chloroplasts with impact on research, health, and
environment. Bioessays. 2016. 37: 1045–1053.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4698130/
3. Zhang H, Rodríguez LAG, Hernández-Díaz S.. Antibiotic Use and the
Risk of Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008; 17:
1308-1315.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18544646/
4. Sameer C. Bactericidal antibiotics induce mitochondrial dysfunction
and oxidative damage in mammalian cells. Sci Transl Med. 2013; 5:
192ra85.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23825301/
5. Granados-Chinchilla F, Rodríguez C. Tetracyclines in Food and
Feeding stuffs: From Regulation to Analytical Methods, Bacterial
Resistance, and Environmental and Health Implications. J Analytical
Methods Chem. 2017: 1315497.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28168081/
6. Nersessian AK, Zilfian Vrez N, Koumkoumadjian VA. Fanardjian.
Inhibitory effect of rat immunization with tularemia vaccine on the in
vivo clastogenicity of 4 anthracycline antibiotics. Mutation Research.
1991; 260: 215-218.
7. Aldre KJ, Kerns RJ, Neil O. Mechanism of Quinolone Action and
Resistance. Biochemistry. 2014: 53: 1585-1574.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24576155/
8. Long H, Miller SF, Strauss C, Zhao C, Cheng L, et al. Antibiotic treatment
enhances the genome-wide mutation rate of target cells. PNAS.
2016; 113: E2498-E2505. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
PMC4983809/ Gonzalez L, Jianne P. Spencer. Aminoglycosides:
A Practical Review Am Fam Physician. 1998; 15; 58:1811-1820.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9835856/
9. Emelyanov VV. Evolutionary relationship of Rickettsiae and
mitochondria. 2001; 501: 11-18.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11457448/
10. Moullan N, et al. Tetracyclines Disturb Mitochondrial Function across
Eukaryotic Models: A Call for Caution in Biomedical Research.” Cell
reports. 2015; 10: 1681-1691.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25772356/
11. Sallmyr A, Feyruz JF, Rassool V. Genomic instability in myeloid malignancies:
Increased reactive oxygen species (ROS), DNA double strand breaks (DSBs)
and error-prone repair. Cancer Letters. 2008; 270: 1-9.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18467025/
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 170https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
12. Hardell L, Carlberg M. Response to Ahlbom et al. Comments on
Hardell and Carlberg Increasing Rates of Brian Tumors in the Swedish
National Inpatient Register and the Causes of Death Register. Int. J.
Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3793–3813.
13. Comments on ROS and P53 gene mutations. P53 non-ionizing radiation
and heat linked specifically to p53 mutation involved in astrocytoma).
14. Liu J, Du J, Zhang Y, Sun W, Smith BJ, et al. Redox Imbalance in
the Development of Colorectal Cancer. J Cancer. 2017; 8:1586–1597.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5535714/
15. Gago-Dominguez M, Castelao JE, Lipid peroxidation and renal cell
carcinoma: Further supportive evidence and new mechanistic insights.
Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2005; 40: 721-733.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16458203/
16. Mufti SI, Nachiappan V, Eskelson CD. Ethanol-mediated promotion of
oesophageal carcinogenesis: association with lipid peroxidation and
changes in phospholipid fatty acid profile of the target tissue. Alcohol
and Alcoholism. 1997; 32:221–231.
17. Martin OCB, Naud N, Taché S, Debrauwer L, Chevolleau S,
et al. Targeting Colon Luminal Lipid Peroxidation Limits Colon
Carcinogenesis Associated with Red Meat Consumption. Cancer Prev
Res (Phila). 2018; 11:569-580.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29954759/
18. Hu W, Feng Z, Eveleigh J, Iyer G, Pan J, et al. The major lipid peroxidation
product, trans- 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, preferentially forms DNA adducts at
codon 249 of human p53 gene, a unique mutational hotspot in hepatocellular
carcinoma, Carcinogenesis. 2002; 23: 1781–1789.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12419825/
19. Zhuo-Lin D, Ma Y. Aflatoxin sufferer and p53 gene mutation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 1998; 4: 28–29.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11819223/
20. Zhang J, Orang’ O, Tonui P, Tong Y, Maina T, et al. Detection and
Concentration of Plasma Aflatoxin Is Associated With Detection of
Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in Kenyan Women. Open Forum
Infectious Diseases. 2019; 6: ofz354.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31392332/
21. Skrzydlewska E, Sulkowski S, Koda M, Zalewski B, Kanczuga-Koda
L, et al.. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in colorectal cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11: 403–406.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4205348/
22. Jinchul K, Lili Y, Xuemei F, Yang X. WTP53 protein known as PUMA
(acronym for “p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis” caused switch
from OP to glycolysis ie Warburg transition). UCLA. 2019.
23. Kathrin S, Keller S, Wolter FE, Röglin L, Beil W, et al. Proximicins A,
B, and C—Antitumor Furan Analogues of Netropsin from the Marine
Actinomycete Verrucosispora Induce Upregulation of p5 3 and the Cyclin
Kinase Inhibitor p21* Angew. Chem Int Ed. 2008; 47: 3258 –3261.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18348121/
24. Mantovani F, Collavin L. Del Sal G. Mutant p53 as a guardian of the
cancer cell. Cell Death Differ. 2019; 26: 199–212.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30538286/
25. Liang Y, Liu J, Feng Z. The regulation of cellular metabolism by tumor
suppressor p53. Cell & Bioscience. 2013; 3.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23388203/
26. Bhaskaran N, Quigley C, Paw C, Butala S, Schneider E, et al. Role
of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Controlling Tregs and Immunopathology
During Mucosal Infection. Front Microbiol. 2018; 9:1995.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30197637/
27. IARC. Biological Agents. 2009; 100.
28. Habbous S, Chu KP, Lau H, Schorr M, Belayneh M, et al. Human
papillomavirus in oropharyngeal cancer in Canada: analysis of 5
comprehensive cancer centres using multiple imputation. CMAJ:
Canadian Medical Association J. 189: E1030–E1040.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5555753/
29. Mégraud F. H pylori antibiotic resistance: prevalence, importance, and
advances in testing. Gut. 2004; 53: 1374–1384.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1774187/
30. Kohanski MA, Tharakan A, Lane AP, Ramanathan M Jr. Bactericidal
antibiotics promote reactive oxygen species formation and inflammation
in human sinonasal epithelial cells. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016; 6:
191-200.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26624249/
31. Ben B, MD et al. Antibiotics increased risk of cancer. Eur J Cancer.
2015; 51: 2655–2664. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26338196/
32. Annamari K, Harri R, Timo K, Eero P, Markku H, et al. Antibiotic predicts
an increased risk of cancer. Wiley-Liss, Inc. 2008; 123: 2152-2155.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18704945/
33. Tim N. Antibiotics may increase the risk of bowel cancer. Medical News
Today. 2017.
34. Sigma M. Penicillin/Streptomycin/Amphotericin B Solution (100X),
Tissue Culture Grade – Calbiochem-harmful and teratogenic and
carcinogenic.
35. Velicer Christine M, Heckbert SR, Lampe JW. Antibiotic Use in
Relation to the Risk of Breast Cancer. JAMA. 2004; 291: 827-835.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14970061/
36. Fraser Gary E, Jaceldo-Siegl K, Orlich M, Mashchak A, Sirirat R, et
al. Dairy, soy, and risk of breast cancer: those confounded milks. Int J
Epidemiol. 2020; dyaa007.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32095830/
37. IARC. Ampicillin was tested for carcinogenicity by oral administration
in mice and rats. It increased the incidences of mononuclear-cell
leukemia and of phaeochromocytomas of the adrenal medulla in male
rats. A slight increase in the incidence of benign lung tumours was
observed in female mice. 1990; 50.
38. Jyrkkanen J. Pesticide Carcinogens in Mothers’ Milk and Total Diet;
An Issue of Motherhood; ... Key Words: breast cancer, carcinogens,
childhood cancers. 2010.
PubMed: https://jorma-jyrkkanen.livejournal.com/142897.html
39. Siegel RL, Torre LA, Soerjomataram I, Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence in young adults. Gut. 2019; 68: 2179-2185.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31488504/
40. Zhao J, Zhu Y, Wang PP, West R, Buehler S, et al. Interaction between
alcohol drinking and obesity in relation to colorectal cancer risk: a case-
control study in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. BMC Public
Health. 2012; 12: 94.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22296784/
41. Taniue K, Hayashi T, Kamoshida Y, Kurimoto A, Takeda Y, et al.
UHRF1-KAT7-mediated regulation of TUSC3 expression via histone
methylation/acetylation is critical for the proliferation of colon cancer
cells. Oncogene. 2020; 39: 1018-1030.
42. Wang X, Moraes CT. Increases in mitochondrial biogenesis impair
carcinogenesis at multiple levels. Molecuar Oncology. 2011; 399-409.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21855427/
43. Chen T. et al. (My comment) Pesticides induced mitochondrial
fragmentation at low levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5751110/
44. Alavanja MCR, Bonner MR. Occupational pesticide exposures and
cancer risk. A review. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2018; 15:
238–263.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22571220/
45. Ray WA, Stein M, May D. Common antibiotic found to pose increased
heart risk. New Engl J Med. 2012.
PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3374857/
46. Giudicessi John R, Ackerman MJ, Azithromycin and Risk of Sudden
Cardiac Death: Guilty as Charged or Falsely Accused? Cleve Clin J
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and
ecosystem risks
https://www.heighpubs.org/jccm 171https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jccm.1001104
Med. 2013; 80: 539–544.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24001961/
47. University of British Columbia. Commonly used antibiotics may lead to
heart problems.” Science Daily. 2019.
www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/09/190910154710.htm
48. FDA. FDA warns some pesticides can cause fatal heart damage. NBC
Health News. 2018.
49. Arias PL, Esteller M. Coding and Non-Coding Genes Silenced
Epigenetically in Cancer. Open Biol. 2017; 7: PMC5627056.
50. Sumei W, et al. Mutual regulation of microRNAs and DNA methylation
in human cancers. Epigenetics. 2017; 12: 187-197.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28059592
51. Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M, Rotter V. Mutations in the p53 Tumor
Suppressor Gene: Important Milestones at the Various Steps of
Tumorigenesis. Genes & cancer. 2011; 2: 466–474.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21779514/
52. Cadernos de Saúde Pública. Brazil Tribal Cancers. Print version ISSN
0102-311XOn-line version ISSN 1678-4464Cad. Saúde Pública. 2019;
35.
53. Raturi A, Simmen T. Where the endoplasmic reticulum and the
mitochondrion tie the knot: The mitochondria-associated membrane
(MAM) Biochemica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Res.
2013; 1833: 213-224.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22575682/
54. Wallace DC. Mitochondria and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012; 12:
685–698.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23001348/
55. Baxter JS, Leavy OC, Dryden NH. et al. Capture Hi-C identifies putative
target genes at 33 breast cancer risk loci. Nat Commun. 2018; 9: 1028.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29531215/
56. Steinberg P. Red meat derived Nitroso Compounds, Lipid Peroxidation
Products and Colorectal Cancer. Foods. 2019. 8: 252.
PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3133678
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
-
Environment Gene Interactions Just another WordPress.com weblog « Chimp Origin of AIDS in Koprowski’s Live Polio Vaccinations of Leopoldvil...
-
Biden-US Govt DOD Funded ECOHEALTH In Wuhan and 46 others in Ukraine 2023-01-30 in possible contravention of the UN Convention Prohibiting ...
-
Mercury Testing on Squamish Chlor-alkali Workers Mercury Testing on Squamish Chlor-alkali Workers 1 January 2012 Mercury An...